Package execution (BizDataX Portal)
After package registration on the BizDataX Portal, the registered package can be executed.
Except on the BizDataX Portal, the package can be executed from Visual Studio (Debug -> Start Debugging (or press F5) or from the command line.
| Table of contents |
|---|
| Package details |
| Package execution start |
| Package execution process |
| Package execution history |
Package details
Registered package contains:
- Package details - main information about the package, filled in the package registration process
- Name
- Package path
- Description
- Package version
- Steps - list of steps defined in BizDataX Designer
- Order
- Name
- Description
- Parameters - list of parameters defined in BizDataX Designer and values set for this execution
- Order
- Name
- Type (boolean, string, int32, double, decimal)
- Default
- Required
- Description
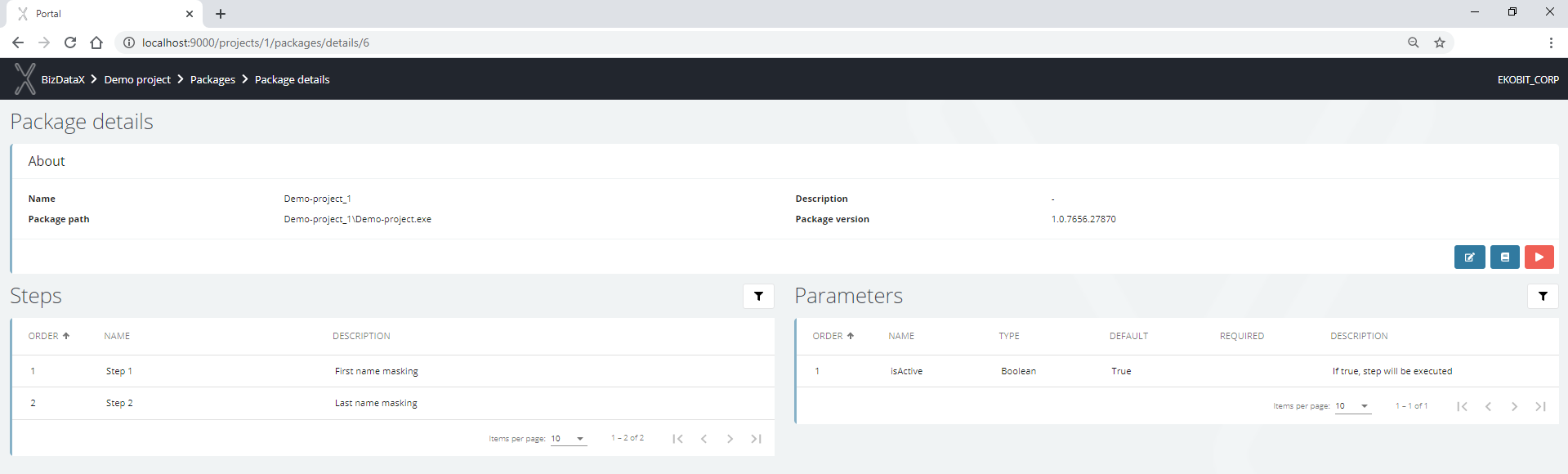 Figure 1: Package details
Figure 1: Package details
Package execution start
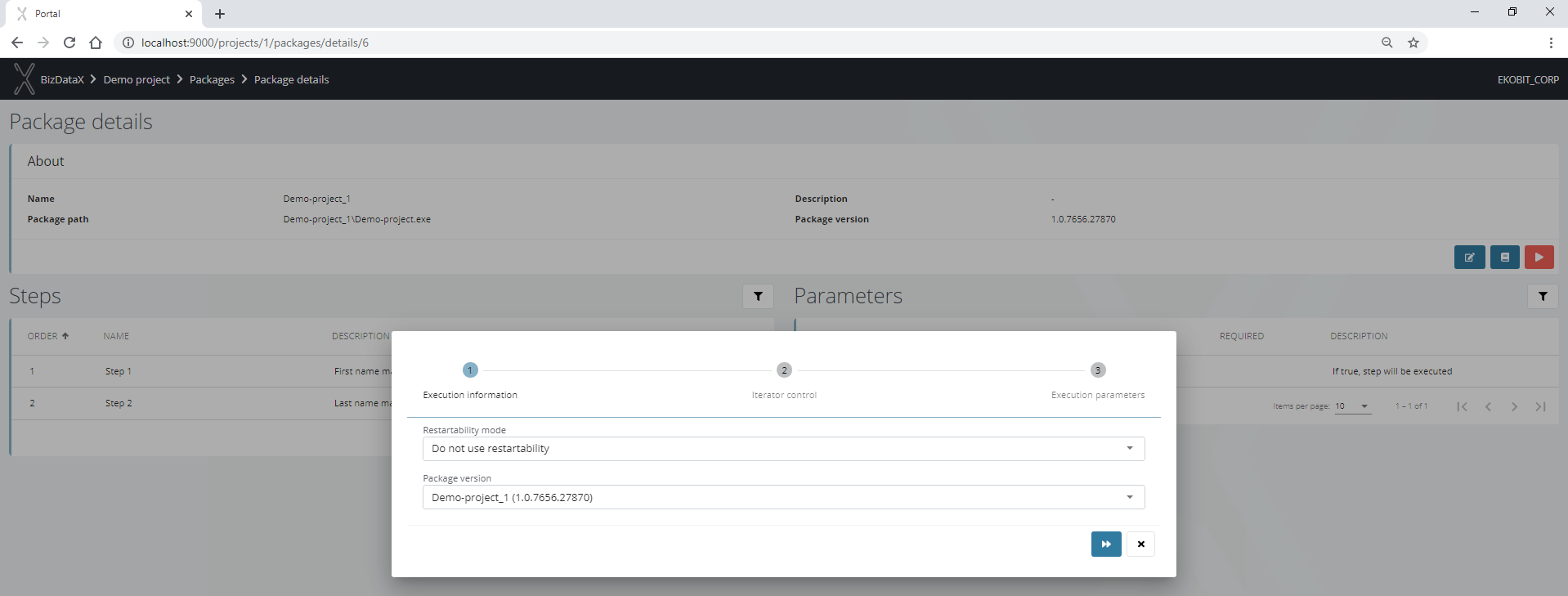
After click on the red play button on the Package details screen, a pop-up wizard for configuring package execution is displayed. In the first step, it is necessary to select the restartability mode and the package version. The restartablity mode must be configured before the package is published and registered.
If the package originated from the same Visual Studio project, ie. was published several times, this means that it appears on the BizDataX Portal in as many packages/versions as it is published, otherwise, the package execution will fail is some mode different than Off is used.
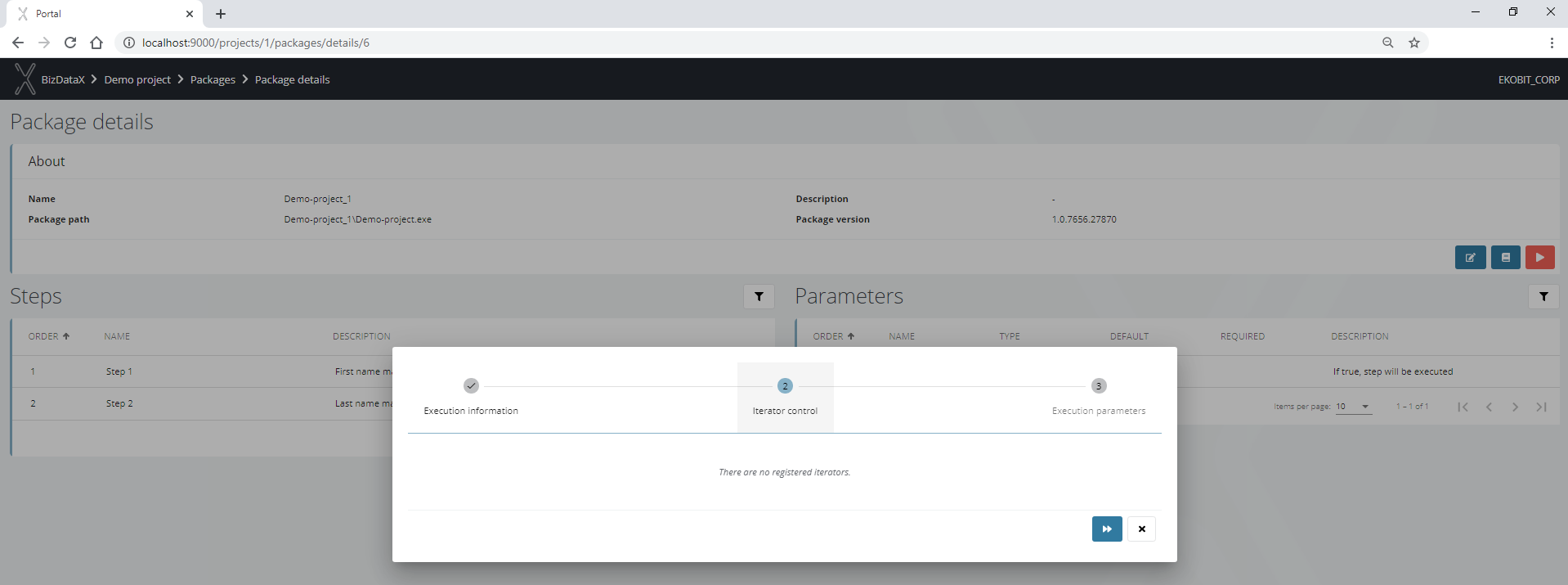
There are no registered iterators in the next step because this package was not previously run through the Portal. Iterators are registered in the BizDataX Portal database when running packages in some of the restartability modes. Each step, partition, and segment defined in BizDataX Designer is registered as an iterator during package execution so the next package execution takes into account only non-finished iterators that the user would specify to execute in this step of the wizard.
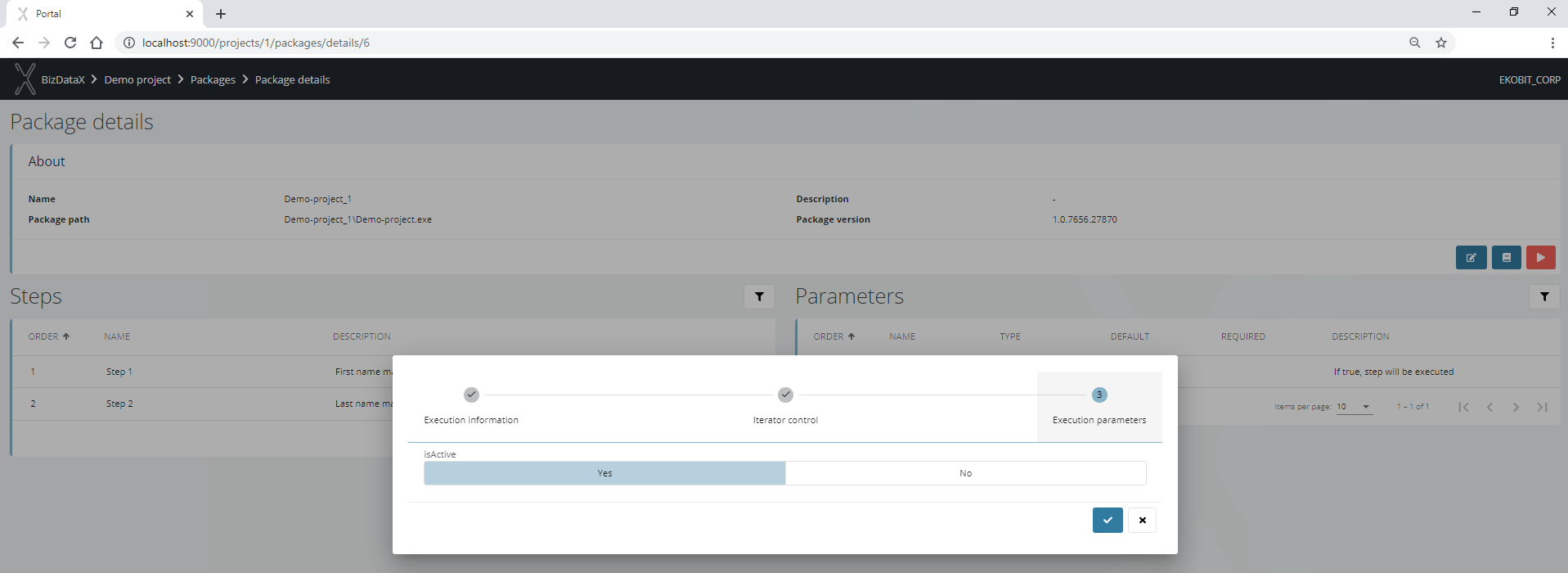
The last step of the wizard determines the values of the parameters defined in BizDataX Designer.
Package execution process
After confirmation, a new page with details about the execution process will be shown. On this page a few blocks appear:
- Execution summary - list of package steps, their names, and statuses, by which you can navigate and see the performance of iterators and engines of each step. Execution can be monitored in real-time by tracking the progress bar, reviewing errors, and tracking logs which can be downloaded containing basic or all content.
Execution can end as:
- completed - the process will be performed as expected.
- failed - the process will end if encounters an unforeseen circumstance.
- aborted - the process will be aborted when the current iterator completes.
- killed - the process will be immediately finished.
- paused - the process will be paused when the current iterator completes and can be resumed at any time.
After successful package execution, the progress bar will be set on 100%, Logs will be created and Execution steps and Table performance will be filled with values for executed steps and masked tables. Execution errors should be empty if everything finished without errors or filled with message errors which should be checked.
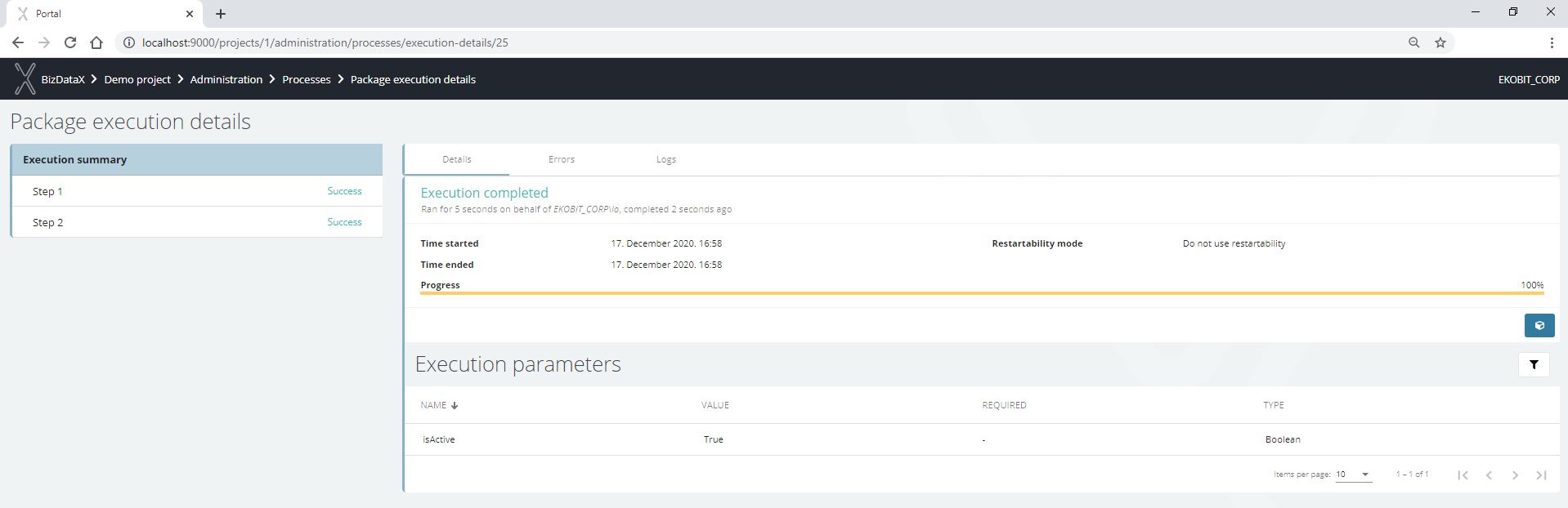 Figure 5: Package execution process - details
Figure 5: Package execution process - details
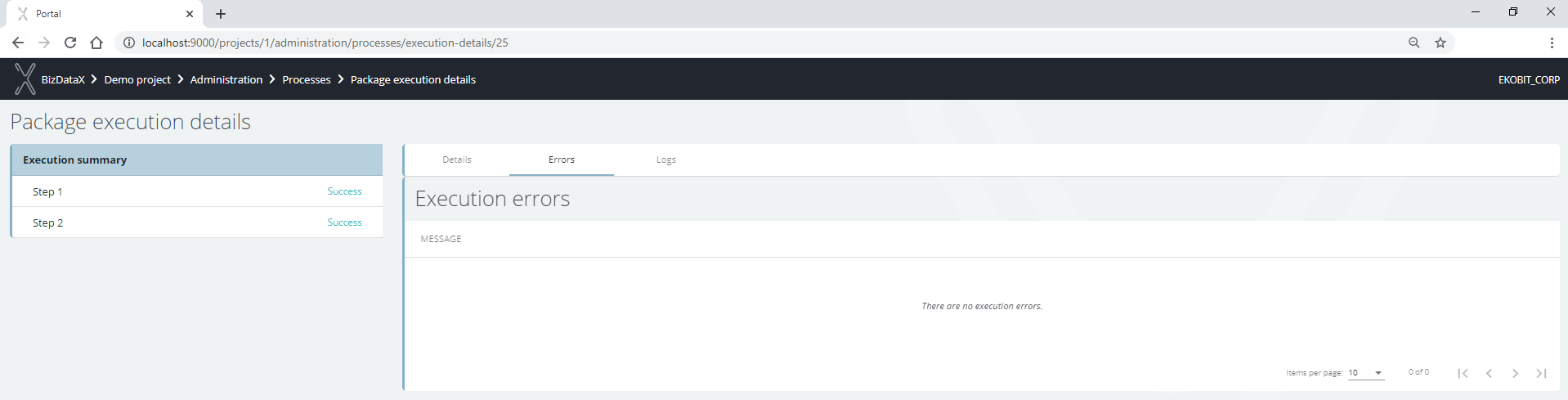 Figure 6: Package execution process - errors
Figure 6: Package execution process - errors
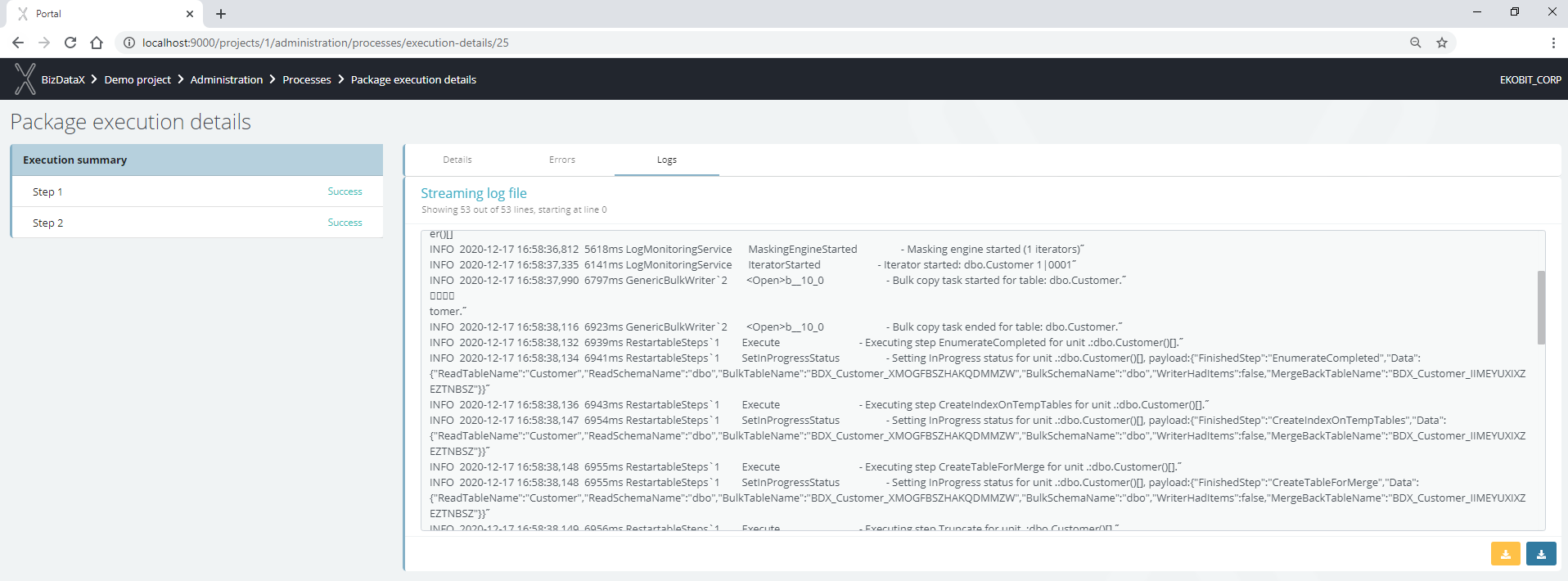 Figure 7: Package execution process - logs
Figure 7: Package execution process - logs
Each step can have multiple iterators where the performance of each of the iterators is monitored by recording the start and end of iterator execution, how many records are processed, how many records are processed per second, and to which engine each iterator belongs.
The step can end as:
- Success - step ended as expected. Its iterators can end as Completed or Skipped.
- Failed - step failed if at least one of its iterators failed. The execution stops and end as Failed as well or continues if ContinueOnIteratorFail parameter is set to
truein the BizDataX Designer properties for the belonging masking engine of that step. - Skipped - because the process ended before performing that step or because the isActive parameter is set to
falsein the BizDataX Designer properties for that step.
The iterator statuses are:
- Completed - iterator ended as expected.
- Failed - iterator execution failed for some reason.
- Scheduled - when the execution of a step begins its iterators get the status Scheduled.
- Running - iterator that is currently running.
- Skipped - in restarted execution this iterator is skipped because it was not selected for execution.
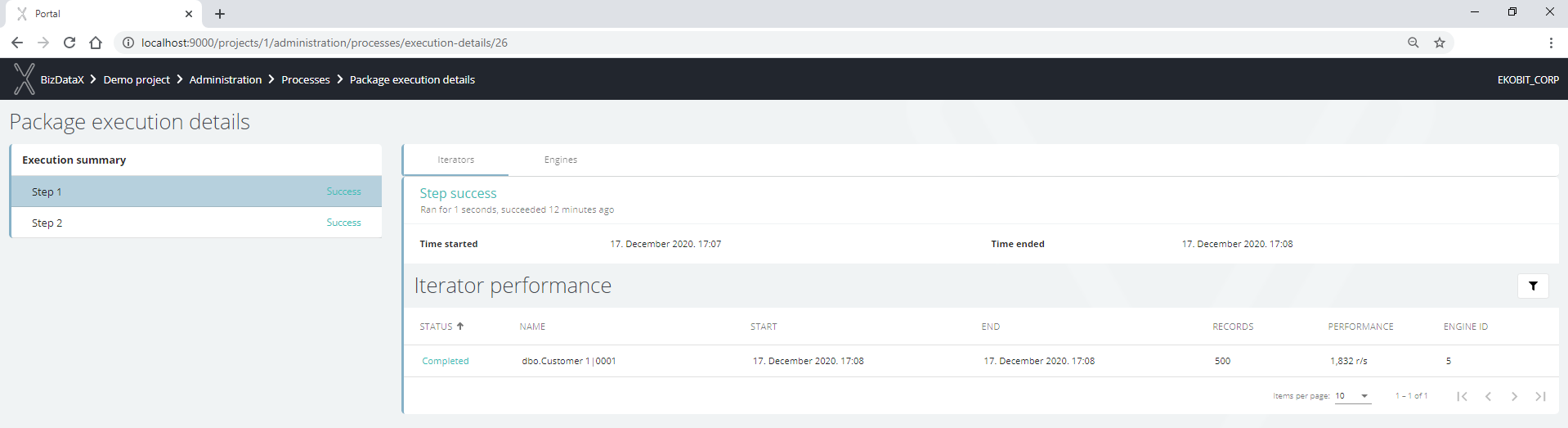 Figure 8: Step - iterator performance
Figure 8: Step - iterator performance
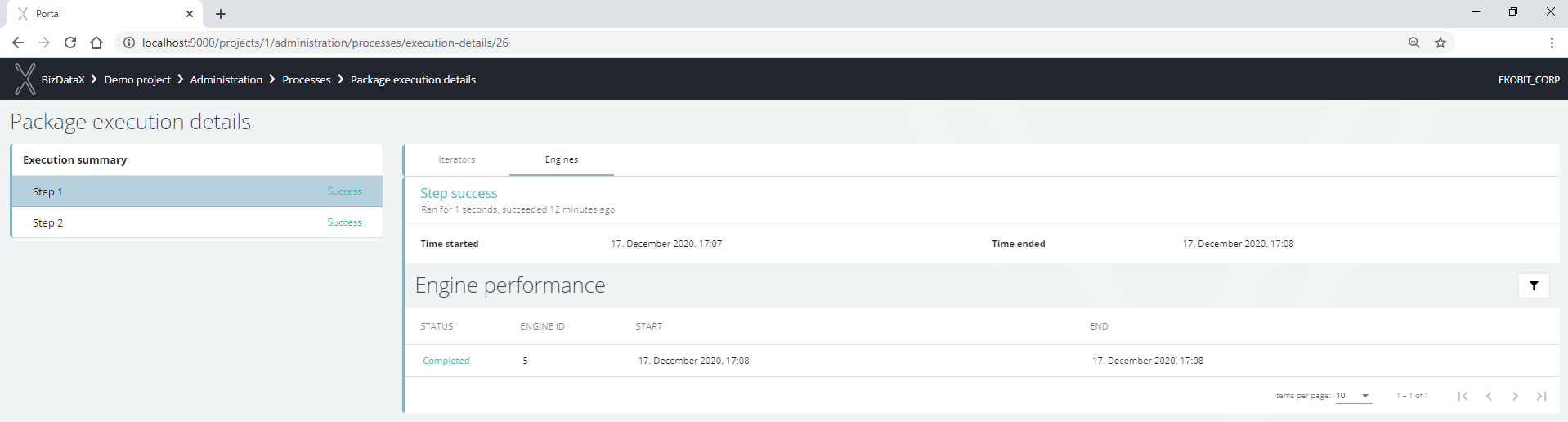 Figure 9: Step - engine performance
Figure 9: Step - engine performance
Package execution history
By selecting Package execution history on the Packages list for the selected package or on the Package details screen, a list of executions for the selected package appears.
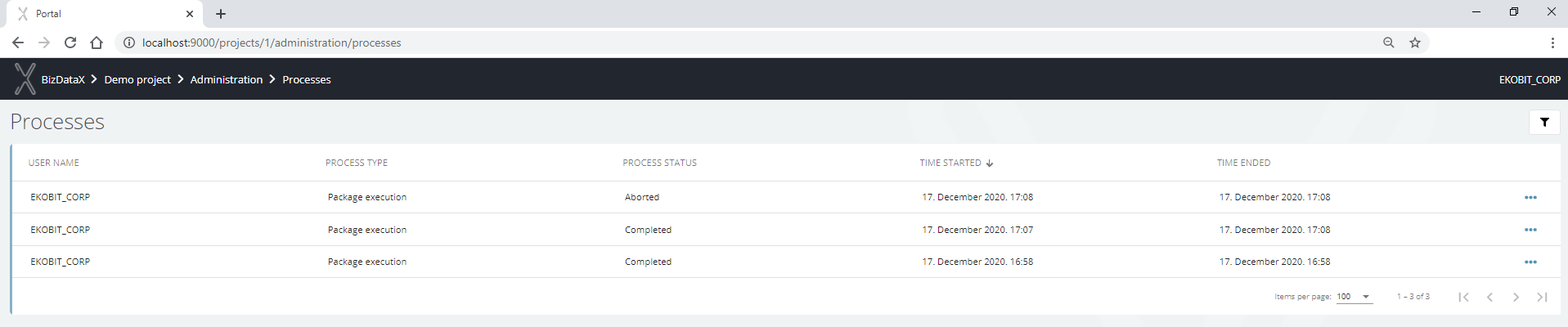 Figure 10: Package execution history
Figure 10: Package execution history
With selecting a specific item from the list, Process details for the selected Package execution appear. Process details are the same as details on the package execution process.